R-Value vs U-Factor: Understanding the Difference for Better Home Insulation
Today, we're diving into the confusing world of insulation measurements - specifically, the showdown between R-value vs U-factor.
The Two Values That Can Transform Your Home
When hunting for the right insulation, you'll bump into two main values that measure thermal performance: R-value and U-factor. These two values might seem like just boring numbers on a product label, but they're actually your secret weapons for creating a comfortable, energy-efficient home!
What's the Deal with R-Value?
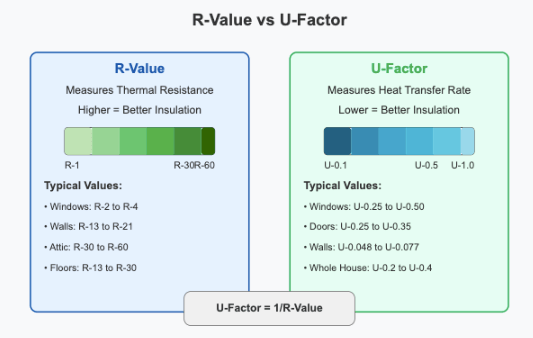
R-value measures thermal resistance - basically, how good a material is at blocking heat flow. Think of R-value as your home's defensive linebacker, tackling heat before it can cross the line.
Higher R-value = Better insulation performance
Common R-value range for walls: R13-R21
Common R-value for attic insulation: R30-R60
R-value is typically the go-to measure for insulation materials like fiberglass, cellulose, and spray foam that fill your wall cavity or cover your attic floor.
U-Factor: The Other Side of the Insulation Coin
While R-value measures a material's resistance to heat transfer, U-factor measures how much heat actually flows through a component or assembly. It's like measuring the actual leaks in your home's thermal envelope rather than just the strength of your barriers.
Lower U-values = Better energy efficiency
U-factor is used for windows, doors, and whole building assemblies
Lower U = less heat loss through your building envelope
U-factor ratings take into account all elements of a component - for example, a window's glass, frame, and spacers - to give you the complete picture of its thermal performance.
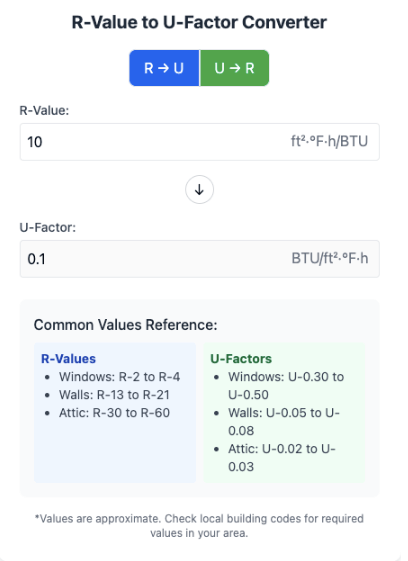
The Mathematical Relationship: They're Reciprocals!
Here's a neat math fact: R-value and U-factor are mathematical reciprocals of each other:
U-factor = 1/R-value
R-value = 1/U-factor
For example:
Insulation with an R-value of 20 has a U-factor of 0.05 (1/20 = 0.05)
A window with a U-factor of 0.30 has an R-value of approximately 3.33 (1/0.30 = 3.33)
Why Two Different Measurements? Not Just to Confuse You!
You might be wondering: "Why do we need two different ways to measure basically the same thing?" Good question! Here's the scoop:
When R-Value Shines:
Measuring individual insulation materials
Comparing different insulation products
Determining insulation thickness needed
Meeting minimum code requirements for insulation
When U-Factor Takes the Stage:
Measuring assembled products like windows
Comparing the energy efficiency of different windows
Determining overall heat loss through building components
Calculating overall building energy performance
The Temperature Difference Factor
Both R-value and U-factor are influenced by temperature difference between inside and outside. This matters because:
Insulation performance can change at different temperatures
Heat flow increases as temperature difference increases
Different materials respond differently to temperature extremes
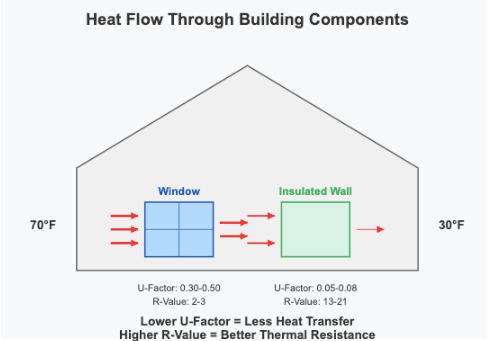
Real-World Example: Windows vs. Walls
Let's compare how these values work in real life:
Typical Wall:
R-value: R-13 to R-21 (depending on construction)
U-factor: 0.077 to 0.048 (1/R-value)
Walls typically use R-value because they're made of layered materials
Typical Window:
U-factor: 0.25 to 0.50 (Energy Star rated)
R-value: 2 to 4 (1/U-factor)
Windows use U-factor because they're complex assemblies
Choosing Between R-Value and U-Factor for Your Home Projects
When tackling your next home improvement project, here's how to know which value to focus on:
Focus on R-value when:
Adding insulation to your attic
Insulating walls during renovation
Selecting insulation materials
Comparing different types of insulation batts or spray foam
Focus on U-factor when:
Replacing windows or doors
Looking at skylights or glass doors
Calculating whole-house energy performance
Comparing different window frame materials
The Measuring Tape of Energy Efficiency
Think of these values like different measuring tapes for your home's energy performance. R-value is like measuring in inches, while U-factor is like measuring in centimeters - they're just different ways to measure the same distance!
What's a Good Number? R-Value and U-Factor Targets
"So what numbers should I be looking for?" I hear you ask. Here's a quick guide:
Good R-values (remember: higher is better):
Walls: R-13 to R-23
Attic: R-30 to R-60
Floors: R-13 to R-30
Good U-factors (remember: lower is better):
Windows in cold climates: 0.30 or lower
Windows in warm climates: 0.40 or lower
Doors: 0.25 or lower
The Insulation Performance Symphony
Getting the right mix of R-values and U-factors throughout your home is like conducting an energy efficiency symphony. Each building component plays its part, and when they work together, the result is beautiful: a comfortable home with reasonable energy bills!
Ask the Insulation Experts
Not sure which insulation will give you the best thermal performance for your specific needs? That's where we come in! At Argyle Bros Insulation, we've seen it all when it comes to insulation challenges. We can help you navigate the confusing world of R-values and U-factors to find the perfect solution for your home.
Here's a little story that might sound familiar: Meet Sarah, who decided to tackle her home's insulation project after watching a few online tutorials. Armed with determination and a measurement tape, she headed to the store and bought insulation with the highest R-value she could afford. Six months later, she was still battling condensation issues and cold spots because she hadn't considered how the U-factor of her windows was affecting her home's overall thermal performance.
Meanwhile, her neighbor Tom called in the professionals who evaluated his entire home as a system, balancing R-values and U-factors throughout. Now Tom enjoys consistent temperatures in every room while Sarah is still adjusting the thermostat every few hours.
The moral? When it comes to home insulation, understanding both R-value and U-factor is like knowing both the offense and defense strategies in football—you need both to win the game! Ready to score a touchdown with your home's energy efficiency? Give us a call at Argyle Bros Insulation. Your comfort (and your utility bills) will thank you!