What is Home Insulation & Why is it Important?
Picture your home as a container for your family's comfort. An uninsulated house is like a colander—you can pour in all the heated or cooled air you want, but it'll slip right through the holes. A properly insulated home is more like a sealed container, keeping your comfort locked in where it belongs. Let's explore why the importance of insulation can't be overstated in creating your perfect home environment.
Understanding How Insulation Works: Your Home's Thermal Shield
Heat flow involves three basic mechanisms: conduction, convection, and radiation. When properly insulating your home, you're addressing all three:
Conduction: Direct heat transfer through materials, like heat moving through your walls
Convection: Heat movement through air, where lighter warmer air rises and cooler denser air sinks
Radiation: Heat traveling in a straight line and heats anything in its path, like sunlight warming your roof
Think of it this way: if you've ever used a vacuum-sealed travel mug, you've seen perfect insulation in action. The same principles that keep your coffee hot for hours can keep your home comfortable all year round.
The Science Behind the Comfort: Understanding R-Values
An insulated wood frame wall might have an r5 ci or r13 rating, while an uninsulated wood frame wall could be as low as r10 ci or r0. But what does this actually mean? The R-value measures resistance to heat flow - the higher the number, the better the insulation performs. Different climate zones require different R-values for optimal performance.
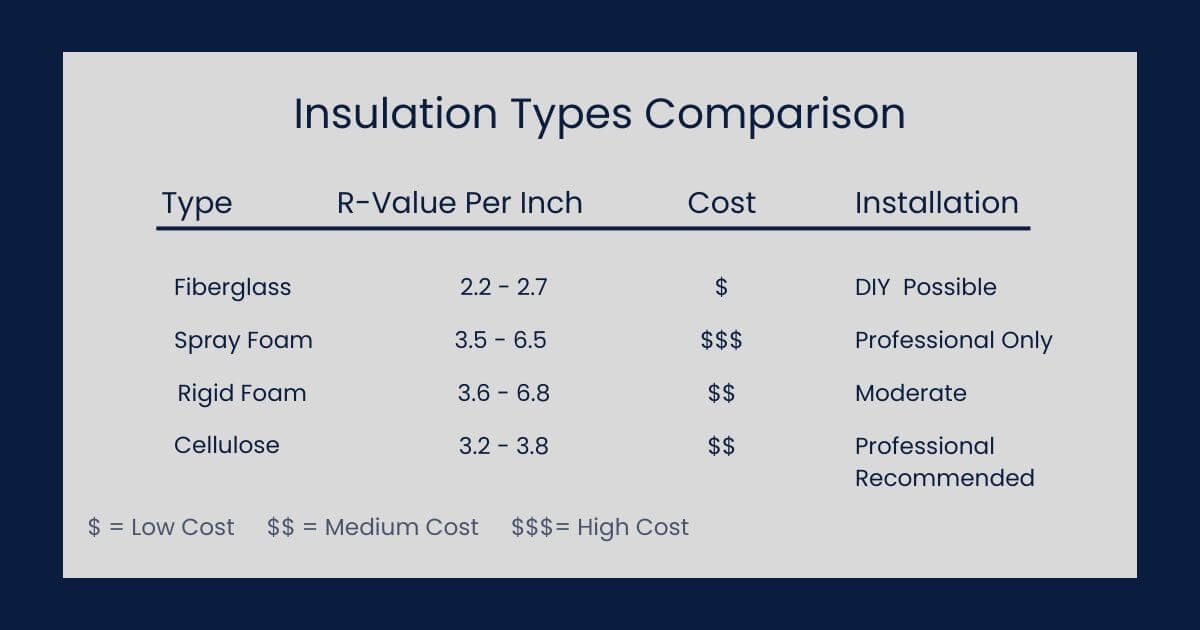
Types of Insulation: Finding Your Perfect Match
Unlike traditional insulation materials, modern options offer incredible versatility. Let's explore each type to help you understand your options:
Fiberglass Insulation
The pink stuff you probably picture when thinking about insulation!, is Fiberglass insulation. It consists of extremely fine glass fibers and is one of the most common insulation materials. It comes in two forms:
Batts and Rolls: Pre-cut panels that fit between wall studs, rafters, and floor joists
Loose Fill: Blown-in material perfect for adding inches of existing attic insulation or filling hard-to-reach spaces
Fiberglass is popular because it's:
Cost-effective
Fire-resistant
Easy to install (though professional installation is recommended)
Excellent at reducing heating and cooling costs
Spray Foam Insulation
Think of spray foam as your home's custom-fit thermal jacket. This modern insulation starts as a liquid that expands into foam, filling every nook and cranny. Available in two types:
Open Cell: Lighter, more flexible, and excellent for sound dampening
Closed Cell: Denser, higher R-value, and creates a moisture barrier
Spray foam excels at:
Slowing conductive heat flow
Creating an air-tight seal
Filling irregular spaces and small gaps
Providing excellent resistance to heat flow
Rigid Foam Boards
These stiff panels of insulation are like your home's thermal shield. Rigid foam boards trap air within their structure, creating an excellent barrier against heat transfer. They come in three main types:
Polyisocyanurate (Polyiso): Highest R-value per inch
Extruded Polystyrene (XPS): Great moisture resistance
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS): Most economical option
Perfect for:
Exterior wall sheathing
Basement walls
Cathedral ceilings
Unvented low-slope roofs
Cellulose Insulation
Made from recycled paper products (primarily newspaper), cellulose is the eco-warrior of insulation materials. It's treated with fire-retardant chemicals for safety and can be:
Dry-blown into attics
Dense-packed into walls
Applied with a wet-spray technique for new construction
Benefits include:
High recycled content
Excellent sound dampening
Great for filling odd-shaped spaces
Lower environmental impact
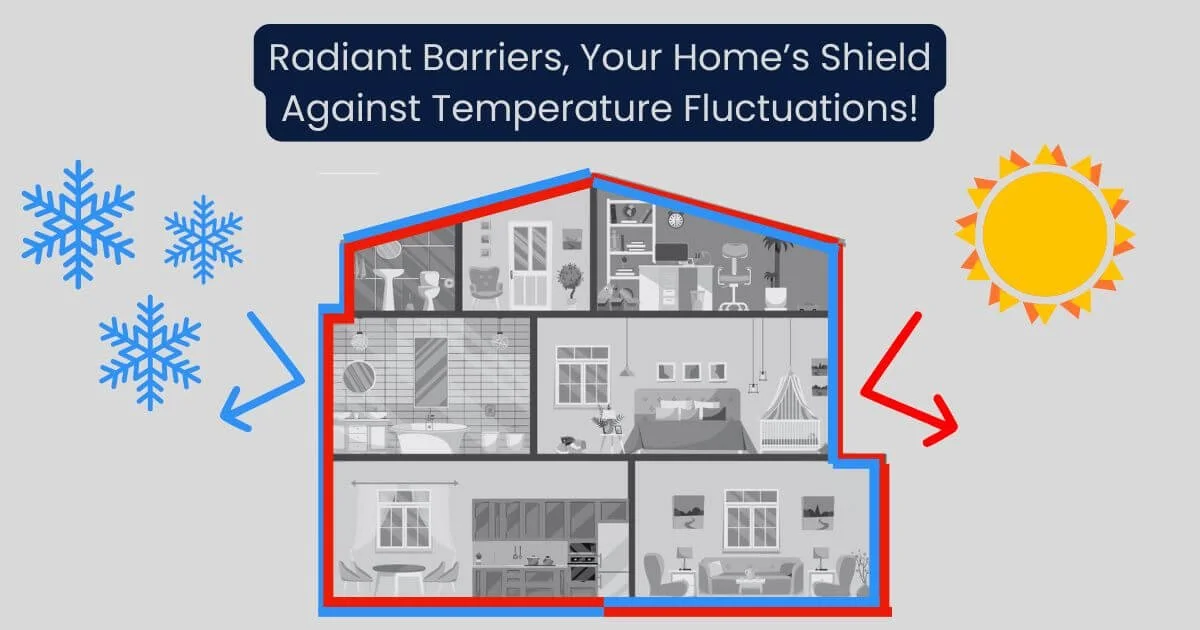
Reflective Insulation Systems and Radiant Barriers
These systems work differently from other types of insulation - instead of slowing heat flow, they reflect radiant heat away from your living space. Think of them as a mirror for heat. They're especially effective in hot climates where cooling costs are a major concern.
Best used in:
Attics
Walls
Around ductwork
Areas with high radiant heat gain
Environmental Impact: Your Home's Green Upgrade
When your heating system and cooling system work less, you're not just saving money:
Reduced carbon footprint
Lower greenhouse gas emissions
Decreased overall energy consumption
Better resource conservation
Professional Installation: The Key to Maximum Benefits
Think of insulation installation like baking a soufflé - the ingredients matter, but the technique makes or breaks the result. Professional installation ensures:
Proper depth and coverage
Correct amounts of continuous insulation
Expert air sealing
Proper handling of life cycle costs recycled materials
Maintenance and Longevity
Quality insulation isn't a one-and-done deal. To maintain peak performance:
Annual inspections for settling or damage
Check for moisture issues
Verify ventilation systems are working properly
Address any gaps or compressed areas
Choosing the Right Solution: Your Decision Guide
Consider these factors when selecting insulation:
Climate zone requirements
Existing insulation condition
Home architecture and design
Budget and ROI expectations
Environmental priorities
The Cost of Waiting
Without proper insulation:
Energy bills can be 30-50% higher
Indoor temperatures fluctuate wildly
HVAC systems wear out faster
Home value suffers
Comfort remains elusive
Real Results: Success Stories
“We have noticed a huge difference after improving our insulation! Our furnace hasn’t had to work as hard and our home doesn’t feel as drafty!”
- A happy customer
FAQ About Home Insulation
What happens if you don't insulate your house?
Without proper insulation, your home becomes an energy sieve. Heat flow moves freely through your walls, making your heating system and cooling system work overtime. Lighter warmer air rises and cooler denser air sinks, creating constant temperature fluctuations. Beyond higher energy bills, you might face:
Inconsistent room temperatures
Cold floors and walls
Potential moisture issues
Higher risk of pipe freezing in winter
Excessive strain on HVAC equipment
Where is insulation most important in a home?
While properly insulating your home means addressing all areas, some spots need special attention:
Attics - Adding inches of existing attic insulation is crucial as heat naturally rises
Exterior Walls - An insulated wood frame wall provides essential resistance to heat flow
Floors Above Unheated Spaces - Helps prevent heat loss through basic mechanisms conduction convection
Crawl Spaces - Often overlooked but vital for energy efficiency
Basements - Especially important for finished living space
How much of a difference does insulation make?
The impact is significant! Properly installed insulation materials resist conductive heat flow and can:
Reduce heating and cooling costs by 15-20%
Decrease energy consumption by up to 30%
Lower your carbon footprint
Improve home comfort dramatically
Extend HVAC equipment life
What are the downsides of insulation?
While the benefits far outweigh any drawbacks, consider:
Initial investment costs (though offset by energy savings)
Importance of professional installation
Need for proper ventilation planning
Regular maintenance requirements
Remember, unlike traditional insulation materials, modern options offer solutions for these challenges, making the downsides manageable with proper planning and installation.
Ready to Transform Your Home?
The importance of insulation extends far beyond comfort - it's an investment in your home's future, your wallet, and our planet. Whether you're dealing with inadequate existing attic insulation or starting fresh, the benefits are clear and compelling.
Ready to seal your home's comfort in, and let your worries leak out? Contact us today for a free consultation and discover how proper insulation can transform your home into the comfortable, efficient space you deserve.